Does Minoxidil Work? Uses, Advantages, Treatmen...
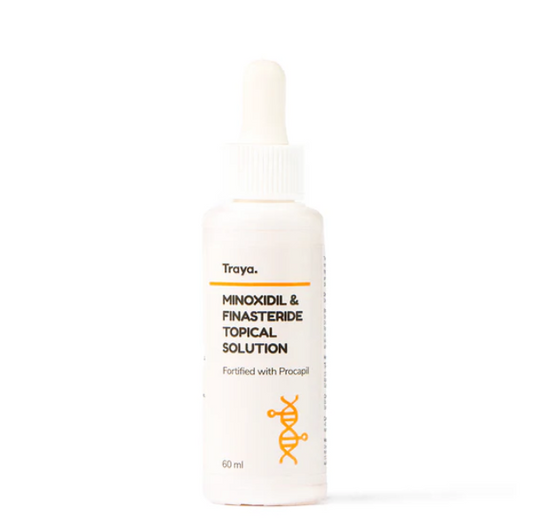
Have you ever wondered how does minoxidil work? With so many products claiming to be the solution for hair loss, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. In this article, we will...
Does Minoxidil Work? Uses, Advantages, Treatmen...
Have you ever wondered how does minoxidil work? With so many products claiming to be the solution for hair loss, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. In this article, we will...

How to prevent white hair, delay greying and ha...
When people think about hair health, they often focus on strands—whether they are falling, thinning, or greying. But what many overlook is the foundation of hair health: the scalp. Scalp...
How to prevent white hair, delay greying and ha...
When people think about hair health, they often focus on strands—whether they are falling, thinning, or greying. But what many overlook is the foundation of hair health: the scalp. Scalp...

Dermatologist or Trichologist: Who should I go ...
Dermatologist or Trichologist ? Who Can Help You With Your Hair Loss Problem? Hair loss is a common hair problem, and you need a dermatologist or skin doctor to take...
Dermatologist or Trichologist: Who should I go ...
Dermatologist or Trichologist ? Who Can Help You With Your Hair Loss Problem? Hair loss is a common hair problem, and you need a dermatologist or skin doctor to take...
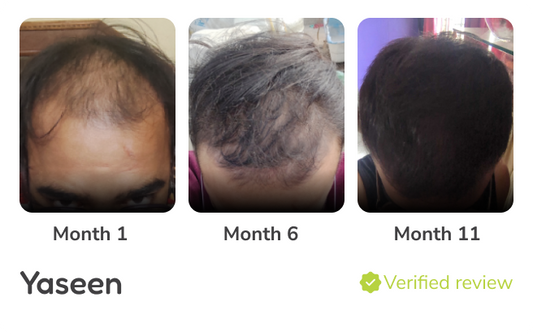
Minoxidil Results - Before and After
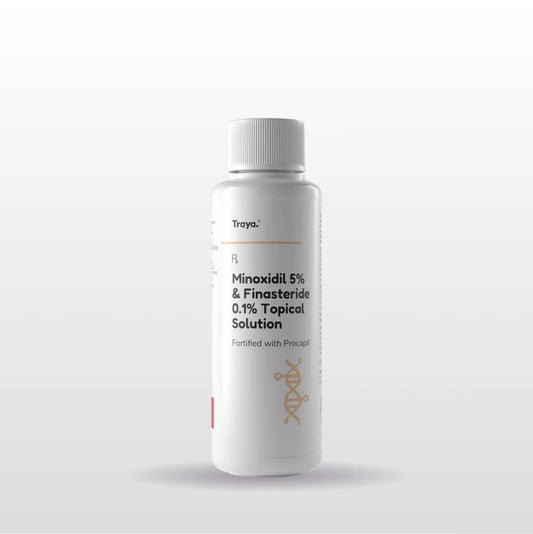
Hair thinning and shedding are the most common hair problems these days. If you are looking for a solution that works wonders and is well-tested, you have made the right...
Minoxidil Results - Before and After
Hair thinning and shedding are the most common hair problems these days. If you are looking for a solution that works wonders and is well-tested, you have made the right...

Stop Grey Hair Using Ayurveda
4 min read
Stop Grey Hair Using Ayurveda
4 min read













