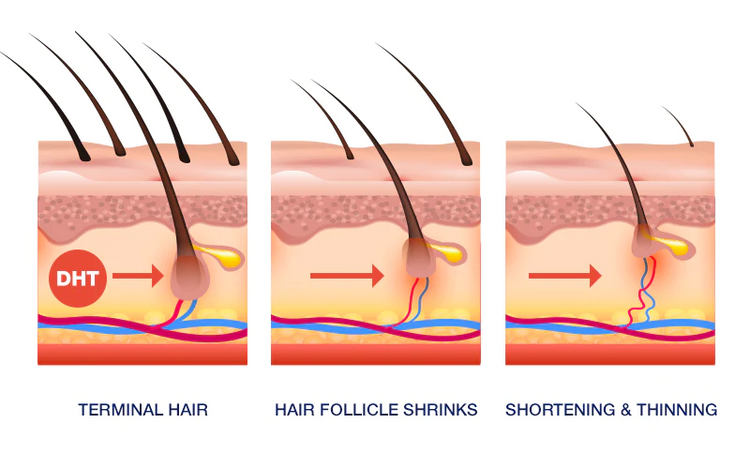
Are you struggling with hair thinning or baldness? The root cause might be something your body produces naturally: DHT (dihydrotestosterone). It’s a byproduct of testosterone and plays a role in overall hormonal function, especially in male development, but also in women’s bodies in smaller amounts. But for many, especially those with a genetic predisposition, it can also trigger hair loss.
DHT binds to receptors in your hair follicles, causing them to shrink over time, a process called miniaturization. Over time, this leads to thinner, weaker strands and, eventually, the follicles may stop producing hair altogether.
While synthetic DHT blockers exist, they often come with side effects like mood swings, hormonal imbalances, or sexual health concerns. That’s why people are now turning to the best natural DHT blocker for hair loss as a safer, more balanced solution.
This guide will walk you through what DHT actually is, how it contributes to hair loss, and the most effective natural ingredients to help block it. From kitchen staples to time-tested herbal remedies, we’ll cover options you can actually use.
What Is DHT, and Why Does It Cause Hair Loss?
DHT stands for dihydrotestosterone. It’s a hormone your body makes from testosterone, using an enzyme called 5-alpha-reductase. DHT is important during puberty, especially for male development.
But when there’s too much DHT later in life, it can affect your hair. It causes hair follicles (the tiny pockets in your scalp where hair grows from) to shrink, which makes the hair thinner and weaker. Over time, this can lead to noticeable hair loss.
That’s why many hair loss treatments aim to lower DHT levels, often by blocking the enzyme that helps make it. This helps protect the hair follicles and slows down the hair loss process.

How DHT Triggers Hair Loss
The problem starts when DHT attaches to androgen receptors (proteins that respond to hormones like testosterone and DHT) located at the base of your hair follicles.
If you're genetically sensitive to DHT, this triggers a slow process called miniaturization, where the follicle gradually shrinks and produces weaker hair over time.
Here’s what happens next:
-
The hair follicle gets smaller
-
Hair grows back thinner and finer with each cycle
-
Eventually, the follicle stops producing visible hair altogether
This process is medically known as androgenetic alopecia, which is often called male-pattern or female-pattern baldness. This does not just lead to visible hair loss, but also results in a gradual decline in hair quality, thickness, and strength over time.
Understanding Gender Differences in DHT Hair Loss
Although more common and pronounced in men, DHT hair loss can also affect women. In men, it shows up as a receding hairline or bald spots on the crown. In women, it appears to be more of an overall thinning, especially at the top of the scalp.
What many don’t realize is that women also produce testosterone (in smaller amounts), which means they also produce DHT. However, their hair follicles may react differently. Female hair loss due to DHT is less about bald patches and more about a loss of density.
What Are DHT Blockers?
DHT blockers are compounds that help reduce the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), either by lowering how much your body makes or by preventing it from attaching to androgen receptors (hormone-sensitive sites in hair follicles). This approach is commonly used to slow down, stop, or even reverse hair loss caused by DHT, known as androgenic alopecia.
DHT blockers work in two main ways:
-
Enzyme Inhibition: Some blockers reduce the activity of 5-alpha-reductase (the enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT), which lowers DHT levels either throughout the body or just in specific areas like the scalp.
-
Receptor Blocking: Others prevent DHT from binding to receptors in the hair follicles, essentially protecting those follicles from DHT’s effects.
Internal vs External DHT Blockers
DHT blockers can be internal or external.
-
Internal blockers include oral medications or dietary supplements. These affect the body's hormonal balance from within, often by targeting DHT production at the root level.
-
External blockers, like DHT-blocking shampoos, oils, or serums, are applied topically to the scalp. They usually contain natural compounds (like saw palmetto, pumpkin seed oil, or caffeine) believed to block DHT locally and improve scalp health.
Drug-Based vs Natural DHT Blockers
One of the most widely used pharmaceutical treatments for DHT-related hair loss is Finasteride, an FDA-approved oral medication. It works by blocking Type II and Type III isoenzymes of 5-alpha-reductase (the enzymes that convert testosterone into DHT), which can lower serum DHT levels (DHT circulating in the blood) by up to 70%.
Another drug, Dutasteride, is even more potent. It inhibits both Type I and Type II isoenzymes, leading to a more significant reduction in DHT production.
However, these medications don’t come without risks. Some people may experience side effects such as:
-
Reduced libido
-
Erectile dysfunction
-
Mood changes
-
Hormonal imbalances
Because of these risks, many people are now exploring natural alternatives. Plant-based compounds such as saw palmetto, pygeum, reishi mushroom, pumpkin seed oil, and nettle root have shown promise for their mild DHT blocker benefits.
If you're wondering how to stop DHT without disrupting your hormonal health, natural DHT blockers might be the safer, long-term route worth considering.
Top Seven Natural DHT Blockers for Hair Loss
Hair loss doesn’t happen overnight, and neither does regrowth. But certain ingredients found in nature show real promise in helping the body handle DHT, the hormone linked with pattern baldness. These natural DHT blockers work in different ways. Some can reduce DHT production, others stop it from attaching to hair follicles.
Here are the best natural DHT blockers for hair loss:
1. Saw Palmetto
What It Is: Saw palmetto is a small, berry-producing plant native to the southeastern United States. It’s commonly found in supplements that support men’s health, particularly for prostate and hormone-related concerns.
How It Works to Reduce DHT: Saw palmetto works by inhibiting 5-alpha-reductase, the enzyme that converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Reducing this enzyme’s activity helps lower DHT levels, which may reduce its impact on hair follicles and slow hair loss.
How to Use It: Mostly found in capsule or tablet form. Some shampoos also include it as a topical ingredient.
Scientific Backing: Saw palmetto acts as a natural DHT blocker, primarily by competitively inhibiting both isoforms of the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This reduces DHT levels and its binding to androgen receptors.
Clinical studies show that saw palmetto can lower serum and tissue DHT levels, leading to mild improvements in hair loss. However, it is less potent than pharmaceutical drugs like finasteride. Its anti-androgenic effects and minimal side effects make it a popular botanical option, but more large-scale clinical trials are needed to confirm its full efficacy for hair regrowth.
2. Pumpkin Seed Oil
What It Is: Extracted from the seeds of pumpkins, this oil is rich in zinc, fatty acids, and phytosterols.
How It Works to Reduce DHT: It may help prevent DHT from binding to androgen receptors in hair follicles, reducing its impact on hair growth.
How to Use It: It is available as a soft gel or liquid supplement. It can also be applied directly to the scalp or mixed into hair oils.
Scientific Backing: Pumpkin seed oil acts as a natural DHT blocker by inhibiting the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT, and contains phytosterols like Δ7-phytosterols that reduce DHT production and androgen receptor activity.
Clinical studies show that daily oral supplementation with 400 mg of pumpkin seed oil for 24 weeks increased hair count by 40% in men with androgenetic alopecia compared to a placebo, with no significant side effects. While evidence is promising, further large-scale human trials are needed to confirm its efficacy for hair growth.
3. Green Tea (EGCG)
What It Is: Made from unoxidized tea leaves, green tea is known for its antioxidant, calming properties. Its core compound is EGCG (Epigallocatechin gallate).
How It Works to Reduce DHT: EGCG helps reduce DHT levels and lowers inflammation in hair follicles.
How to Use It: Drink 1-2 cups daily or use EGCG-infused hair serums. Green tea rinses are also gaining popularity.
Scientific Backing: Research has shown that epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a major polyphenol in green tea, can selectively inhibit 5-alpha-reductase activity. This supports its potential to promote hair growth by stimulating the proliferation and survival of human dermal papilla cells (DPCs).
4. Reishi Mushroom
What It Is: It is also called Ganoderma lucidum. This medicinal mushroom has been used in East Asia for centuries.
How It Works to Reduce DHT: It acts as a natural anti-androgen by inhibiting 5-alpha-reductase and potentially lowering DHT levels.
How to Use It: Available in capsules, powders, or tinctures. It can be brewed with tea or added to smoothies.
Scientific Backing: Research suggests that ganoderol B, a compound found in Reishi mushroom, may inhibit 5-alpha-reductase and influence androgen receptor activity, potentially reducing DHT’s impact at the cellular level. These effects have been observed in animal studies and human cancer cell lines, though not yet confirmed in hair follicle-specific research.
5. Nettle Root
What It Is: A plant traditionally used in herbal medicine, especially for joint pain and urinary issues.
How It Works to Reduce DHT: Nettle root may not significantly reduce DHT production, but it appears to limit its binding to androgen receptors, particularly in prostate tissue.
How to Use It: Commonly taken as a tincture, capsule, or herbal tea. Some shampoos also feature nettle root as a scalp-active botanical.
Scientific Backing: Studies have demonstrated that nettle root extract reduced 5‑alpha‑reductase activity, which prevented testosterone from converting into DHT in the prostate. This same research found that the extract helps limit DHT’s interaction with hormonal receptors, potentially reducing androgen activity at the tissue level.
6. Spearmint Tea
What It Is: A cooling, minty herbal tea with hormonal balancing effects.
How It Works to Reduce DHT: It helps lower free testosterone, which means there’s less available to convert into DHT.
How to Use It: Drink 1-2 cups per day. It’s a popular choice among women dealing with hormonal acne and thinning hair.
Scientific Backing: In women with androgen excess (such as those with PCOS or hirsutism), spearmint tea has shown anti-androgenic effects by significantly reducing levels of free and total testosterone. This includes the fraction available to convert into DHT.
7. Fenugreek Extract
What It Is: A spice commonly used in Indian kitchens, known for its slightly bitter, maple-syrup-like scent.
How It Works to Reduce DHT: It may modulate hormone levels and slow the conversion of testosterone to DHT.
How to Use It: Fenugreek seeds can be soaked and eaten, or ground into a paste and applied to the scalp. Capsules and powders are also widely available.
Scientific Backing: Studies found that supplementation with 500 mg of fenugreek extract daily over eight weeks resulted in a 9‑10% decrease in serum DHT levels. Notably, there were no significant changes in free testosterone or estrogen, suggesting targeted modulation without broad hormonal disruption.
The search for the natural DHT blockers doesn’t have to be confusing. From foods that block DHT, like fenugreek and reishi mushroom, to plant-based topicals such as saw palmetto and green tea extracts, there are options for every lifestyle.
DHT Blocker Benefits Beyond Hair
While most people turn to DHT blockers to fight hair thinning and male-pattern baldness, their benefits can go beyond just the scalp. Whether you choose natural options or prescription medications, managing DHT levels may have several effects on your overall well-being, such as:
1. Less Scalp Inflammation
High DHT levels can irritate hair follicles, causing redness, itching, and inflammation. Using internal supplements alongside DHT-blocking shampoos may help reduce these symptoms by lowering local DHT activity and creating a healthier environment for hair growth.
2. Slower Hair Thinning
The biggest DHT blocker benefit is slowing down follicle shrinkage. This delays hair thinning and helps maintain hair volume over time. It also supports stronger regrowth.
3. Improves Seborrheic Dermatitis
Some natural DHT blockers like green tea or reishi may help reduce excess oil and flakes. This can improve scalp conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis, which can worsen hair loss.
4. Supports Prostate Health (In Men)
Too much DHT is linked to benign prostatic hyperplasia or also known as BPH, which is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. Studies suggest that natural DHT blockers like saw palmetto or nettle root may help reduce BPH symptoms and promote better urinary health.
While the best natural DHT blockers for hair loss can be effective, they typically work over time, not overnight. Unlike prescription options like finasteride, which may deliver faster results but often come with side effects, herbal or plant-based blockers are gentler and generally better tolerated by most individuals.
However, they require patience and consistency. Results may take 3 to 6 months or longer, depending on the severity of the hair loss and how your body responds to the treatment.
Common Myths About DHT and Hair Loss
DHT is one of the most misunderstood hormones when it comes to hair. Here's a look at some common myths and why they don’t hold up.
Myth 1: All DHT is Harmful
Here’s where many get it wrong: DHT isn’t all bad. It plays an essential role in:
-
Maintaining a healthy sex drive
-
Supporting prostate health
-
Building muscle
-
Regulating mood and cognition
So, when people ask, ‘Does DHT cause hair loss?’ The answer is yes, but only in hair follicles that are sensitive to it. Blocking all DHT can create other health issues. That’s why people often look for ways to reduce its effects only on the scalp, not throughout the whole body.
Myth 2: DHT Blockers Stop Hair Loss Overnight
People often expect quick results, but hair regrowth takes time. Even the most reliable blockers take months to show visible change. Even with the best treatments, you may only notice changes after 3-6 months. Natural DHT blockers work gradually by reducing follicle damage, not instantly reversing hair loss.
Myth 3: Only Men Need to Block DHT
Women also produce DHT, though in smaller amounts. In cases of hormonal imbalance or conditions like PCOS, DHT-related hair thinning is common among women. So, DHT blocker benefits apply to women too. Ignoring this can delay helpful treatments and worsen the condition.
Myth 4: Topical Blockers Are as Effective as Oral
Topicals like DHT-blocking shampoos help on the scalp surface but can’t reach internal hormone levels like oral supplements or medications. Both play a role in lowering DHT hair loss, but they work differently and have different strengths.
Ayurvedic & Herbal DHT Blockers
India’s traditional system of medicine offers a wide range of ayurvedic DHT blockers that support hair health while gently addressing hormonal imbalances. These remedies aim to restore the body’s internal balance over time, making them ideal for consistent, long-term use.
1. Bhringraj
Bhringraj has earned its title as ‘King of Hair’ in Ayurveda for a reason. It is deeply nourishing to the scalp, promotes better blood circulation, and helps reduce hair fall. It can be applied in oil form, added to hair masks, or even used as a dried powder mixed with other herbs. Regular use helps strengthen the roots and stimulate hair follicles.
2. Amla
Amla is rich in vitamin C and antioxidants. It helps regulate hormonal activity and supports collagen production, which is essential for strong hair strands. Amla is commonly consumed as a powder, juice, or even taken in capsule form. It is also a staple in herbal oils for topical use.
3. Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is a powerful adaptogen that helps reduce cortisol levels, the body’s stress hormone. Elevated cortisol can increase androgen activity, including DHT, which contributes to hair loss. By balancing stress, ashwagandha indirectly helps regulate androgens. It can be consumed in powder or capsule form and is often paired with warm milk or herbal teas.
4. Licorice Root
Licorice root (Mulethi) works in two ways: it reduces androgen levels and soothes scalp inflammation. Its anti-androgenic properties make it a gentle natural DHT blocker. Whether consumed as tea or used in oil infusions, licorice root helps promote a healthier scalp environment and hair regrowth.
Ayurvedic Combinations for Better Results
Ayurveda rarely depends on a single herb. Instead, it promotes synergy between herbs. Combinations such as Amla + Bhringraj oil or Ashwagandha + Licorice tea often work better than any one ingredient alone. Mixing herbs with healthy fats or warm liquids also improves absorption and effectiveness.
Unlike synthetic drugs, these natural DHT blockers don’t cause abrupt changes in the body. They slowly move your system toward hormonal harmony, making them safe for prolonged use without harsh side effects. This makes them suitable for both men and women dealing with DHT-related hair issues.
Can Diet Help Block DHT?
The relationship between food and hormones is more powerful than most people realize. What we eat directly influences hormone production, inflammation, and nutrient levels. This plays a big role in how much DHT is produced and how it affects the body, especially the scalp.
Foods That Naturally Support DHT Regulation
Certain foods that block DHT are rich in nutrients that either reduce DHT conversion or help maintain a healthier hormonal balance. Here are some of them:
-
Pumpkin seeds are high in zinc and phytosterols. They are known to inhibit 5-alpha reductase, the enzyme that turns testosterone into DHT.
-
Flaxseeds provide lignans and omega-3 fatty acids, which support hormone detoxification and reduce inflammation.
-
Berries, like blueberries and strawberries, are packed with antioxidants that protect hair follicles from oxidative stress.
-
Chickpeas, lentils, and cashews are excellent sources of zinc, a core mineral for hormone regulation and scalp health.
-
Green vegetables such as spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in magnesium, iron, and antioxidants. These leafy greens also reduce oxidative stress, improving the environment for hair follicles.
-
Magnesium plays an essential role in testosterone metabolism, which indirectly helps in keeping DHT levels in check.
What to Avoid for Lower DHT
It is also equally important to avoid foods that may raise DHT levels:
-
Diets high in red meat and saturated fats may raise testosterone levels, potentially leading to increased DHT conversion in some individuals.
-
High-sugar diets cause insulin spikes and inflammation, which further disturb hormonal balance and may lead to hair loss.
-
Processed foods and fried items can also contribute to hormonal disruption and poor scalp health.
In short, foods rich in healthy fats and cholesterol, such as fish, eggs, nuts, and red meat, support testosterone production. Some of this testosterone is naturally converted into DHT by 5-alpha-reductase. Nutrients like zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D also play a crucial role in regulating these hormonal processes and keeping levels in check.
Eating too little fat can lower testosterone levels, as cholesterol is required to make hormones. On the other hand, consuming high amounts of saturated fats and cholesterol may raise testosterone. This, in turn, increases DHT levels, which could contribute to hair loss in those who are genetically sensitive to it. Therefore, balanced fat intake is important for maintaining hormonal health.
Lastly, the best approach is eating a balanced diet with enough healthy fats and nutrients to support normal hormone production while avoiding too much processed food and sugar, which can throw off your hormone balance.
FAQs
1. Can women take DHT blockers?
While DHT blockers are often marketed to men, women also produce small amounts of DHT, which can cause DHT hair loss. In many cases, supplements or topicals like DHT blocking shampoo are used by women experiencing thinning hair, especially around the crown or hairline. It’s important to choose gentle options, as hormone levels in women are more sensitive. So, to answer the question, women can also enjoy DHT blocker benefits.
2. Do DHT blockers really work?
They can work consistently overtime. DHT blockers work by interfering with the conversion of testosterone into DHT, which is the hormone most commonly linked to hair follicle shrinkage. While individual results vary, many people using natural DHT blockers for hair loss have reported reduced hair shedding and signs of new growth within a few months.
3. How long until I see results?
Patience is important here. Most people start noticing results from eating foods that block DHT and taking supplements around the 90-day mark. Some see reduced hair fall earlier, while visible regrowth might take a bit longer. Hair grows in cycles, so it may take time for stronger strands to push through. Stick with it, and track small signs like reduced shedding while washing or combing.
4. Are there side effects to natural blockers?
Most natural options are generally well tolerated. However, anything that affects hormones can trigger subtle changes. Some people experience DHT blocker side effects like mild scalp irritation, particularly when using topical DHT blockers combined with herbs such as saw palmetto or nettle. If combining multiple products, it's always a good idea to monitor how your body responds.
5. Can I combine DHT blockers with Minoxidil or Redensyl?
Yes, and it’s actually a common approach to block DHT naturally. A DHT blocker for men targets the hormone responsible for hair loss, while topical treatments like Minoxidil or Redensyl work to stimulate new hair growth. Just make sure to introduce one product at a time, so you can track how each one behaves with your scalp and hair.
Final Thoughts
Hair loss doesn’t happen overnight, and neither does recovery. But once you understand how DHT affects your hair, you're in a much better position to take meaningful steps. Using the best natural DHT blockers for hair loss can be a helpful part of that process. These plant-based options work gently, supporting scalp health without the harsh side effects that often come with stronger medications.
Still, lasting results take more than just DHT blockers alone. What you eat, how your body processes hormones, and even your stress levels all influence your hair health. That’s why it’s important to look at the full range of DHT blocker benefits, not just topical solutions, but internal support too. Managing DHT from the inside out, through better nutrition and consistent care, is what truly helps create lasting change.
And that’s exactly what Traya is built around. We don’t believe in quick fixes; we focus on treating the root cause. Our treatment combines the strengths of Ayurveda, Dermatology, and Nutrition to address every factor contributing to your hair loss. Because when you treat the root, you give your hair the best chance to grow back stronger, healthier, and sustainably.
Take the Traya hair test to find out what’s really causing your hair loss, and get a plan that treats it from the root.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278957/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430924/
- https://ishrs.org/dht-blockers-hair-loss/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513329/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15510237/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11124163/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10648974/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4017725/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3252722/